Chapter 7 Feature History for ASA 5505 Interfaces Cisco ASA 5500 Series Configuration Guide using the CLI 7-14 Starting Interface Configuration (ASA 5505) Page 293. CH A P T E R 8 Completing Interface Configuration (Routed Mode) This chapter includes tasks to complete the interface configuration for all models in routed firewall mode. View and Download Cisco ASA 5505 hardware installation manual online. Adaptive Security Appliance. ASA 5505 Firewall pdf manual download. In this post I have gathered the most useful Cisco ASA Firewall Commands and created a Cheat Sheet list that you can download also as PDF at the end of the article. I have been working with Cisco firewalls since 2000 where we had the legacy PIX models before the introduction of the ASA 5500 and the newest ASA 5500-X series. PDF On May 25, 2016, Motasem Hamdan and others published Cisco ASA firewall command line Technical Guide.
- Cisco Asa 5506 X Setup
- Asa 5505 Datasheet
- Cisco Asa 5510 Manual
- Cisco Asa 5505 Manual Pdf
- Cisco Asa 5505 Pdf
- Cisco Asa 5505 Manual Pdf Download
- Cisco Asa 5505 User Manual Pdf
Do you know which is the default console password for asa 5505? I tried different combinations, searching over the internet but nothing worked. The default enable password of an unconfigured ASA or an ASA configured with factory defaults is empty, so you had just to hit enter. Chapter 4 Installing the ASA 5505. PoE Ports and Devices. PoE Ports and Devices. On the ASA 5505, switch ports Ethernet 0/6 and Ethernet 0/7 support PoE devices that are compliant with the IEEE 802.3af standard, such as IP phones and wireless access points.
Cisco ASA 5505 User Manual, 1994 pages| Recognized languages: | English |
|---|---|
| Pages: | 1994 |
| Size: | 22.87 MB |
- Getting Started with the ASA
- Introduction to the Cisco ASA 5500 Series
- New Features
- Firewall Functional Overview
- Security Policy Overview
- Getting Started
- Configuring ASDM Access for Appliances
- Starting ASDM
- Factory Default Configurations
- ASA 5505 Default Configuration
- Working with the Configuration
- Saving Configuration Changes
- Managing Feature Licenses
- Supported Feature Licenses Per Model
- Information About Feature Licenses
- Time-Based Licenses
- Shared AnyConnect Premium Licenses
- Failover Licenses (8.3(1) and Later)
- Configuring Licenses
- Configuring a Shared License
- Monitoring Licenses
- Introduction to the Cisco ASA 5500 Series
- Configuring Firewall and Security Context Modes
- Configuring the Transparent or Routed Firewall
- Configuring the Firewall Mode
- Information About the Firewall Mode
- Configuring ARP Inspection for the Transparent Firewall
- Configuring ARP Inspection
- Customizing the MAC Address Table for the Transparent Firewall
- Configuring the MAC Address Table
- Firewall Mode Examples
- How Data Moves Through the ASA in Routed Firewall Mode
- How Data Moves Through the Transparent Firewall
- Configuring the Firewall Mode
- Configuring Multiple Context Mode
- Information About Security Contexts
- Context Configuration Files
- How the ASA Classifies Packets
- Management Access to Security Contexts
- Information About Resource Management
- Information About MAC Addresses
- Configuring Multiple Contexts
- Enabling or Disabling Multiple Context Mode
- Managing Security Contexts
- Reloading a Security Context
- Monitoring Security Contexts
- Viewing Assigned MAC Addresses
- Information About Security Contexts
- Configuring the Transparent or Routed Firewall
- Configuring Interfaces
- Starting Interface Configuration (ASA 5510 and Higher)
- Information About Starting ASA 5510 and Higher Interface Configuration
- Management Interface
- Redundant Interfaces
- EtherChannels
- Starting Interface Configuration (ASA 5510 and Higher)
- Configuring a Redundant Interface
- Configuring an EtherChannel
- Configuration Examples for ASA 5510 and Higher Interfaces
- Information About Starting ASA 5510 and Higher Interface Configuration
- Starting Interface Configuration (ASA 5505)
- Information About ASA 5505 Interfaces
- Starting ASA 5505 Interface Configuration
- Configuration Examples for ASA 5505 Interfaces
- Completing Interface Configuration (Routed Mode)
- Information About Completing Interface Configuration in Routed Mode
- Completing Interface Configuration in Routed Mode
- Configuring IPv6 Addressing
- Configuration Examples for Interfaces in Routed Mode
- Completing Interface Configuration (Transparent Mode)
- Information About Completing Interface Configuration in Transparent Mode
- Completing Interface Configuration in Transparent Mode
- Configuring IPv6 Addressing
- Starting Interface Configuration (ASA 5510 and Higher)
- Configuring Basic Settings
- Configuring Basic Settings
- Configuring the Hostname, Domain Name, and Passwords
- Setting the Date and Time
- Configuring the Master Passphrase
- Monitoring DNS Cache
- Configuring DHCP
- Configuring a DHCP Server
- Configuring DHCP Options
- Configuring a DHCP Server
- Configuring Dynamic DNS
- Configuration Examples for DDNS
- Configuring Basic Settings
- Configuring Objects and Access Lists
- Configuring Objects
- Configuring Objects and Groups
- Information About Objects and Groups
- Configuring Objects
- Configuring Object Groups
- Configuring Regular Expressions
- Scheduling Extended Access List Activation
- Configuring Objects and Groups
- Information About Access Lists
- Adding an Extended Access List
- Configuring Extended Access Lists
- Configuration Examples for Extended Access Lists
- Adding an EtherType Access List
- Configuring EtherType Access Lists
- Adding a Standard Access List
- Adding Standard Access Lists
- Adding a Webtype Access List
- Using Webtype Access Lists
- Adding an IPv6 Access List
- Configuring IPv6 Access Lists
- Configuring Logging for Access Lists
- Configuring Logging for Access Lists
- Managing Deny Flows
- Configuring Objects
- Configuring IP Routing
- Routing Overview
- Information About Routing
- Supported Route Types
- How Routing Behaves Within the ASA
- Information About the Routing Table
- How the Routing Table Is Populated
- Information About IPv6 Support
- Information About Routing
- Configuring Static and Default Routes
- Configuring Static and Default Routes
- Configuring a Static Route
- Configuring a Default Static Route
- Configuring Static and Default Routes
- Defining Route Maps
- Information About Route Maps
- Customizing a Route Map
- Configuring OSPF
- Customizing OSPF
- Configuring RIP
- Information About RIP
- Configuring RIP
- Customizing RIP
- Configuring Multicast Routing
- Information About Multicast Routing
- Multicast Group Concept
- Customizing Multicast Routing
- Configuring IGMP Features
- Configuring PIM Features
- Additional References
- Information About Multicast Routing
- Configuring EIGRP
- Configuring EIGRP
- Customizing EIGRP
- Configuring Interfaces for EIGRP
- Configuring IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
- Information About IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
- Additional References
- Routing Overview
- Configuring Network Address Translation
- Information About NAT
- NAT Types
- Static NAT
- Dynamic NAT
- Dynamic PAT
- NAT in Routed and Transparent Mode
- How NAT is Implemented
- Routing NAT Packets
- NAT Types
- Configuring Network Object NAT
- Configuring Network Object NAT
- Configuration Examples for Network Object NAT
- Configuring Twice NAT
- Configuring Twice NAT
- Configuration Examples for Twice NAT
- Information About NAT
- Configuring Service Policies Using the Modular Policy Framework
- Configuring a Service Policy Using the Modular Policy Framework
- Information About Service Policies
- Default Settings
- Task Flows for Configuring Service Policies
- Identifying Traffic (Layer 3/4 Class Maps)
- Configuration Examples for Modular Policy Framework
- Configuring Special Actions for Application Inspections (Inspection Policy Map)
- Configuring a Service Policy Using the Modular Policy Framework
- Configuring Access Control
- Configuring Access Rules
- Information About Access Rules
- General Information About Rules
- Information About Extended Access Rules
- Information About EtherType Rules
- Information About Access Rules
- Configuring AAA Servers and the Local Database
- Information About AAA
- RADIUS Server Support
- RSA/SDI Server Support
- LDAP Server Support
- Using Certificates and User Login Credentials
- Configuring AAA
- Adding a User Account to the Local Database
- Differentiating User Roles Using AAA
- Additional References
- Information About AAA
- Configuring the Identity Firewall
- Information About the Identity Firewall
- Task Flow for Configuring the Identity Firewall
- Monitoring the Identity Firewall
- Configuring Management Access
- Configuring ASA Access for ASDM, Telnet, or SSH
- Configuring CLI Parameters
- Configuring ICMP Access
- Configuring Management Access Over a VPN Tunnel
- Configuring AAA for System Administrators
- Information About AAA for System Administrators
- Configuring Authentication to Access Privileged EXEC Mode (the enable Command)
- Configuring Command Authorization
- Configuring AAA Rules for Network Access
- Configuring Authentication for Network Access
- Information About Authentication
- Authenticating Directly with the ASA
- Configuring Authorization for Network Access
- Configuring RADIUS Authorization
- Configuring Authentication for Network Access
- Configuring Filtering Services
- Configuring ActiveX Filtering
- Licensing Requirements for ActiveX Filtering
- Configuring Java Applet Filtering
- Filtering URLs and FTP Requests with an External Server
- Configuring Additional URL Filtering Settings
- Monitoring Filtering Statistics
- Configuring Web Cache Services Using WCCP
- Configuring Digital Certificates
- Information About Digital Certificates
- Trustpoints
- Revocation Checking
- The Local CA
- Prerequisites for Local Certificates
- Configuring Digital Certificates
- Configuring Local CA Certificate Characteristics
- Information About Digital Certificates
- Configuring Access Rules
- Configuring Application Inspection
- Getting Started with Application Layer Protocol Inspection
- Information about Application Layer Protocol Inspection
- Configuring Inspection of Basic Internet Protocols
- DNS Inspection
- Configuring DNS Rewrite
- FTP Inspection
- HTTP Inspection
- Instant Messaging Inspection
- IP Options Inspection
- IPsec Pass Through Inspection
- IPv6 Inspection
- NetBIOS Inspection
- SMTP and Extended SMTP Inspection
- DNS Inspection
- Configuring Inspection for Voice and Video Protocols
- CTIQBE Inspection
- H.323 Inspection
- Verifying and Monitoring H.323 Inspection
- MGCP Inspection
- RTSP Inspection
- SIP Inspection
- Skinny (SCCP) Inspection
- Configuring Inspection of Database and Directory Protocols
- Sun RPC Inspection
- Configuring Inspection for Management Application Protocols
- DCERPC Inspection
- GTP Inspection
- RADIUS Accounting Inspection
- SNMP Inspection
- Getting Started with Application Layer Protocol Inspection
- Configuring Unified Communications
- Information About Cisco Unified Communications Proxy Features
- Configuring the Cisco Phone Proxy
- Information About the Cisco Phone Proxy
- Prerequisites for the Phone Proxy
- Prerequisites for Rate Limiting TFTP Requests
- End-User Phone Provisioning
- Phone Proxy Guidelines and Limitations
- Configuring the Phone Proxy
- Configuring Linksys Routers with UDP Port Forwarding for the Phone Proxy
- Troubleshooting the Phone Proxy
- IP Phone Registration Failure
- Configuration Examples for the Phone Proxy
- Configuring the TLS Proxy for Encrypted Voice Inspection
- Information about the TLS Proxy for Encrypted Voice Inspection
- Configuring the TLS Proxy for Encrypted Voice Inspection
- Configuring Cisco Mobility Advantage
- Information about the Cisco Mobility Advantage Proxy Feature
- Mobility Advantage Proxy Deployment Scenarios
- Configuring Cisco Mobility Advantage
- Configuration Examples for Cisco Mobility Advantage
- Information about the Cisco Mobility Advantage Proxy Feature
- Configuring Cisco Unified Presence
- Information About Cisco Unified Presence
- Configuring Cisco Unified Presence Proxy for SIP Federation
- Configuration Example for Cisco Unified Presence
- Configuring Cisco Intercompany Media Engine Proxy
- Information About Cisco Intercompany Media Engine Proxy
- Architecture and Deployment Scenarios for Cisco Intercompany Media Engine
- Configuring Cisco Intercompany Media Engine Proxy
- Information About Cisco Intercompany Media Engine Proxy
- Configuring Connection Settings and QoS
- Configuring Connection Settings
- Information About Connection Settings
- Guidelines and Limitations
- Configuring Connection Settings
- Monitoring Connection Settings
- Configuration Examples for Connection Settings
- Configuring QoS
- Information About QoS
- Configuring QoS
- Configuring a Service Rule for Traffic Shaping and Hierarchical Priority Queuing
- Monitoring QoS
- Configuring Connection Settings
- Configuring Advanced Network Protection
- Configuring the Botnet Traffic Filter
- Information About the Botnet Traffic Filter
- Botnet Traffic Filter Databases
- Configuring the Botnet Traffic Filter
- Monitoring the Botnet Traffic Filter
- Configuration Examples for the Botnet Traffic Filter
- Information About the Botnet Traffic Filter
- Configuring Threat Detection
- Configuring Basic Threat Detection Statistics
- Configuring Advanced Threat Detection Statistics
- Configuring Scanning Threat Detection
- Using Protection Tools
- Configuring IP Audit for Basic IPS Support
- Configuring the Botnet Traffic Filter
- Configuring Modules
- Configuring the ASA IPS Module
- Information About the ASA IPS module
- Configuring the ASA IPS module
- Configuring Basic IPS Module Network Settings
- Troubleshooting the ASA IPS module
- Configuring the ASA CX Module
- Information About the ASA CX Module
- Information About ASA CX Management
- Configuring the ASA CX Module
- Monitoring the ASA CX Module
- Troubleshooting the ASA CX Module
- General Recovery Procedures
- Information About the ASA CX Module
- Configuring the ASA CSC Module
- Information About the CSC SSM
- Configuring the CSC SSM
- Troubleshooting the CSC Module
- Configuring the ASA IPS Module
- Configuring High Availability
- Information About High Availability
- Failover System Requirements
- Failover and Stateful Failover Links
- Stateful Failover Link
- Active/Active and Active/Standby Failover
- Stateless (Regular) and Stateful Failover
- Auto Update Server Support in Failover Configurations
- Failover Health Monitoring
- Failover Messages
- Configuring Active/Standby Failover
- Information About Active/Standby Failover
- Configuring Active/Standby Failover
- Configuring Optional Active/Standby Failover Settings
- Controlling Failover
- Configuring Active/Active Failover
- Information About Active/Active Failover
- Configuring Active/Active Failover
- Configuring Optional Active/Active Failover Settings
- Remote Command Execution
- Controlling Failover
- Information About High Availability
- Configuring VPN
- Configuring IPsec and ISAKMP
- Information About Tunneling, IPsec, and ISAKMP
- Configuring ISAKMP
- Enabling IPsec over NAT-T
- Configuring Certificate Group Matching for IKEv1
- Configuring IPsec
- Configuring L2TP over IPsec
- Information About L2TP over IPsec/IKEv1
- Configuring L2TP over IPsec
- Setting General VPN Parameters
- Permitting Intra-Interface Traffic (Hairpinning)
- Understanding Load Balancing
- Comparing Load Balancing to Failover
- Some Typical Mixed Cluster Scenarios
- Configuring Load Balancing
- Frequently Asked Questions About Load Balancing
- Configuring Connection Profiles, Group Policies, and Users
- Connection Profiles
- Configuring Connection Profiles
- Configuring Remote-Access Connection Profiles
- Configuring LAN-to-LAN Connection Profiles
- Configuring Connection Profiles for Clientless SSL VPN Sessions
- Configuring Microsoft Active Directory Settings for Password Management
- Configuring the Connection Profile for RADIUS/SDI Message Support for the AnyConnect Client
- Group Policies
- Configuring Group Policies
- Supporting a Zone Labs Integrity Server
- Configuring Integrity Server Support
- Configuring User Attributes
- Configuring Attributes for Specific Users
- Configuring IP Addresses for VPNs
- Configuring an IP Address Assignment Method
- Configuring Remote Access IPsec VPNs
- Configuring Remote Access IPsec VPNs
- Configuring Network Admission Control
- Configuring a NAC Policy
- Changing Global NAC Framework Settings
- Changing Clientless Authentication Settings
- Configuring Easy VPN Services on the ASA 5505
- Specifying the Mode
- Specifying the Tunnel Group or Trustpoint
- Guidelines for Configuring the Easy VPN Server
- Configuring the PPPoE Client
- Configuring LAN-to-LAN IPsec VPNs
- Configuring ISAKMP Policy and Enabling ISAKMP on the Outside Interface
- Creating a Crypto Map and Applying It To an Interface
- Configuring Clientless SSL VPN
- Observing Clientless SSL VPN Security Precautions
- Using SSL to Access the Central Site
- Configuring Application Helper
- Using Single Sign-on with Clientless SSL VPN
- Configuring SSO Authentication Using SiteMinder
- Configuring SSO Authentication Using SAML Browser Post Profile
- Configuring SSO with the HTTP Form Protocol
- Encoding
- Creating and Applying Clientless SSL VPN Policies for Accessing Resources
- Using the Security Appliance Authentication Server
- Configuring Browser Access to Plug-ins
- Providing Access to Third-Party Plug-ins
- Providing Access to a Citrix Java Presentation Server
- Understanding How KCD Works
- Configuring KCD
- Configuring Application Access
- Logging Off Smart TunnelConfiguring Smart Tunnel Access
- Automating Smart Tunnel Access
- Logging Off Smart Tunnel
- Configuring Port Forwarding
- Assigning a Port Forwarding List
- Application Access User Notes
- Recovering from hosts File Errors When Using Application Access
- Configuring File Access
- CIFS File Access Requirement and Limitation
- Using E-Mail over Clientless SSL VPN
- Optimizing Clientless SSL VPN Performance
- Configuring Content Transformation
- Clientless SSL VPN End User Setup
- Defining the End User Interface
- Customizing Clientless SSL VPN Pages
- Applying Customizations to Connection Profiles, Group Policies and Users
- Configuring Browser Access to Client-Server Plug-ins
- About Installing Browser Plug-ins
- Preparing the Security Appliance for a Plug-in
- Customizing Help
- Configuring Remote Systems to Use Clientless SSL VPN Features
- Translating the Language of User Messages
- Capturing Data
- Configuring AnyConnect VPN Client Connections
- Guidelines and Limitations
- Configuring AnyConnect Connections
- Translating Languages for AnyConnect User Messages
- Configuring Advanced AnyConnect Features
- Configuring AnyConnect Host Scan
- Host Scan Dependencies and System Requirements
- Installing and Enabling Host Scan on the ASA
- Configuring IPsec and ISAKMP
- Configuring Logging, SNMP, and Smart Call Home
- Configuring Logging
- Information About Logging
- Configuring Logging
- Configuring an Output Destination
- Configuring NetFlow Secure Event Logging (NSEL)
- Information About NSEL
- Configuring NSEL
- Monitoring NSEL
- Additional References
- Configuring SNMP
- Information About SNMP
- SNMP Version 3
- Configuring SNMP
- Troubleshooting Tips
- Monitoring SNMP
- Configuration Examples for SNMP
- Additional References
- Information About SNMP
- Configuring Anonymous Reporting and Smart Call Home
- Information About Anonymous Reporting and Smart Call Home
- Information About Anonymous Reporting
- Configuring Anonymous Reporting and Smart Call Home
- Configuring Smart Call Home
- Information About Anonymous Reporting and Smart Call Home
- Configuring Logging
- System Administration
- Managing Software and Configurations
- Managing the Flash File System
- Downloading Software or Configuration Files to Flash Memory
- Performing Zero Downtime Upgrades for Failover Pairs
- Backing Up Configuration Files or Other Files
- Using a Script to Back Up and Restore Files
- Configuring Auto Update Support
- Downgrading Your Software
- Troubleshooting
- Testing Your Configuration
- Performing Password Recovery
- Other Troubleshooting Tools
- Managing Software and Configurations
- Reference
- Using the Command-Line Interface
- Text Configuration Files
- Addresses, Protocols, and Ports
- IPv4 Addresses and Subnet Masks
- Subnet Masks
- IPv6 Addresses
- IPv6 Address Types
- IPv4 Addresses and Subnet Masks
- Configuring an External Server for Authorization and Authentication
- Configuring an External LDAP Server
- Organizing the ASA for LDAP Operations
- Defining the ASA LDAP Configuration
- Active Directory/LDAP VPN Remote Access Authorization Examples
- Configuring an External RADIUS Server
- Configuring an External LDAP Server
- Using the Command-Line Interface

Table of Contents
Note Read the safety warnings in the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (RCSI), and follow proper safety procedures when performing the steps in this guide. See http://www.cisco.com/go/asadocs for links to the RCSI and other documents.
1. Verifying the Package Contents
2. Installing the Chassis
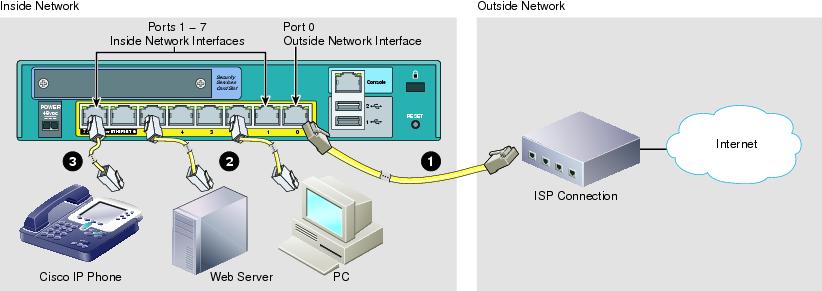
The ASA ships with a default configuration that includes two preconfigured networks (the Inside network and the Outside network) and an Inside interface configured for a DHCP server. Clients on the Inside network obtain a dynamic IP address from the ASA so that they can communicate with each other as well as with devices on the Internet.
Step 1 Connect one end of an Ethernet cable (not provided) to Ethernet 0 on the ASA. (By default, Ethernet 0 is the Outside interface.) Connect the other end to a cable/DSL modem or gateway router (the Outside network).
Step 2 Connect your devices (such as PCs, printers, and servers) with Ethernet cables to Ethernet 1 through 7.
Note Connect a PC to the ASA so that you can run the Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM). See “4. Initial Configuration Considerations.”
Step 3 Connect Power over Ethernet (PoE) devices (such as Cisco IP Phones or network cameras) with Ethernet cables to switch ports 6 or 7 (the only ports providing power to PoE devices).
If you connect a server (such as a web server) to the ASA, you can use ASDM to make services on that server accessible by internal and external users. See “7. (Optional) Allowing Access to Public Servers Behind the ASA.”
3. Powering on and Verifying Interface Connectivity
Step 1 Connect the power supply adaptor to the power cable.
Step 2 Connect the rectangular connector of the power supply adaptor to the power connector on the rear panel of the ASA.
Step 3 Connect the AC power connector of the power cable to an electrical outlet. (The ASA does not have a power switch. Completing this step powers on the device.)
Step 4 Check the Power LED on the front of the ASA; if it is solid green, the device is powered on.
Step 5 Check your management PC to make sure it received an IP address on the 192.168.1.0/24 network using DHCP.
Step 6 Check the LINK/ACT indicators to verify interface connectivity.
Interface Connectivity
Each Ethernet interface has an LED to indicate a physical link is established. When the LED is solid green, a link is established. When the LED is flashing green, there is network activity.
If a LINK/ACT LED is not lit, the link could be down due to a duplex mismatch. If auto-negotiation is disabled, verify you are using a straight-through Ethernet cable.
For a description of all chassis components, see the hardware installation guide on Cisco.com.
4. Initial Configuration Considerations
The ASA ships with a default configuration that, in most cases, is sufficient for your basic deployment. You configure the ASA by using ASDM. ASDM is a graphical interface that allows you to manage the ASA from any location by using a web browser.
However, changing certain settings is recommended or required. For example, you should change the following settings from their defaults:
- The privileged EXEC mode (enable) password that is required to administer the ASA through ASDM and the CLI
- When using the ASA as a VPN endpoint (using the SSL VPN features):
– The hostname, domain name, and DNS server names
– Outside interface IP address to a static address
– Identity certificate
– WINS names when access to Windows file shares is required
Use the Startup Wizard in ASDM to make these changes. See “6. Running the Startup Wizard.”
Cisco Asa 5506 X Setup
5. Launching ASDM
Asa 5505 Datasheet
See the ASDM release notes on Cisco.com for the requirements to run ASDM.
Step 1 On the PC connected to the ASA, launch a web browser.
Step 2 In the Address field, enter the following URL:
https://192.168.1.1/admin
The Cisco ASDM web page appears.
Step 3 Click Run Startup Wizard.
Step 4 Accept any certificates according to the dialog boxes that appear. The Cisco ASDM-IDM Launcher appears.
Step 5 Leave the username and password fields empty and click OK.
The main ASDM window appears and the Startup Wizard opens. See “6. Running the Startup Wizard.”
6. Running the Startup Wizard
Run the Startup Wizard to modify the default configuration so that you can customize the security policy to suit your deployment. Using the startup wizard, you can set the following:
|
|
Step 1 If the wizard is not already running, in the main ASDM window, choose Wizards > Startup Wizard.
Cisco Asa 5510 Manual
Step 2 Follow the instructions in the Startup Wizard to configure your ASA.
Step 3 While running the wizard, you can accept the default settings or change them as required. (For information about any wizard field, click Help.)
7. (Optional) Allowing Access to Public Servers Behind the ASA
The Public Server pane automatically configures the security policy to make an inside server accessible from the Internet. As a business owner, you might have internal network services, such as a web and FTP server, that need to be available to an outside user. You can place these services on a separate network behind the ASA, called a demilitarized zone (DMZ). By placing the public servers on the DMZ, any attacks launched against the public servers do not affect your inside networks.
Cisco Asa 5505 Manual Pdf
Step 1 In the main ASDM window, choose Configuration > Firewall > Public Servers. The Public Server pane appears.
Step 2 Click Add, then enter the public server settings in the Add Public Server dialog box. (For information about any field, click Help.)
Step 3 Click OK. The server appears in the list.
Step 4 Click Apply to submit the configuration to the ASA.
8. (Optional) Running VPN Wizards
Cisco Asa 5505 Pdf
You can configure VPN using the following wizards:
- Site-to-Site VPN Wizard—Creates an IPsec site-to-site tunnel between two ASAs.
- AnyConnect VPN Wizard—Configures SSL VPN remote access for the Cisco AnyConnect VPN client. AnyConnect provides secure SSL connections to the ASA for remote users with full VPN tunneling to corporate resources. The ASA policy can be configured to download the AnyConnect Client to remote users when they initially connect via a browser. With AnyConnect 3.0 and later, the client can run either the SSL or IPSec IKEv2 VPN protocol.
- Clientless SSL VPN Wizard—Configures clientless SSL VPN remote access for a browser. Clientless, browser-based SSL VPN lets users establish a secure, remote-access VPN tunnel to the ASA using a web browser. After authentication, users access a portal page and can access specific, supported internal resources. The network administrator provides access to resources by users on a group basis. ACLs can be applied to restrict or allow access to specific corporate resources.
- IPsec (IKEv1) Remote Access VPN Wizard—Configures IPsec VPN remote access for the Cisco IPsec client.
Cisco Asa 5505 Manual Pdf Download
Step 1 In the main ASDM window, choose Wizards > VPN Wizards, then choose one of the following:
- Site-to-Site VPN Wizard
- AnyConnect VPN Wizard
- Clientless VPN Wizard
- IPsec (IKEv1) Remote Access VPN Wizard
Cisco Asa 5505 User Manual Pdf
Step 2 Follow the wizard instructions. (For information about any wizard field, click Help.)